What are the raw materials of polyester yarn?
2025-07-10
As a key raw material with a production volume of over 30% in the textile industry, the composition and characteristics of polyester yarn directly determine the performance of the final product. Unlike cotton yarn, which relies on natural cotton, the raw materials of polyester yarn come from the petrochemical industry chain and have the remarkable characteristics of stable industrial production and controllable performance.

Core raw materials: the chemical nature of polyester chips
The direct raw material of polyester yarn is polyester chips, which is a white granular solid with a chemical name of polyethylene terephthalate (PET), which is synthesized by polycondensation of terephthalic acid (PTA) and ethylene glycol (EG). For every ton of polyester chips produced, about 0.85 tons of PTA and 0.33 tons of EG are consumed. Both of these basic chemical raw materials come from petroleum refining products - PTA is made by oxidation of paraxylene (PX), and EG is mostly extracted from ethylene cracking products.
The quality index of polyester chips has a significant impact on the performance of polyester yarn. The intrinsic viscosity (IV value) needs to be controlled between 0.63-0.68dL/g. Too high will lead to spinning difficulties, and too low will affect the yarn strength. The ash content of high-quality chips must be less than 50ppm to ensure that the spinneret is not blocked during the spinning process.
Raw material processing: Conversion process from chips to yarns
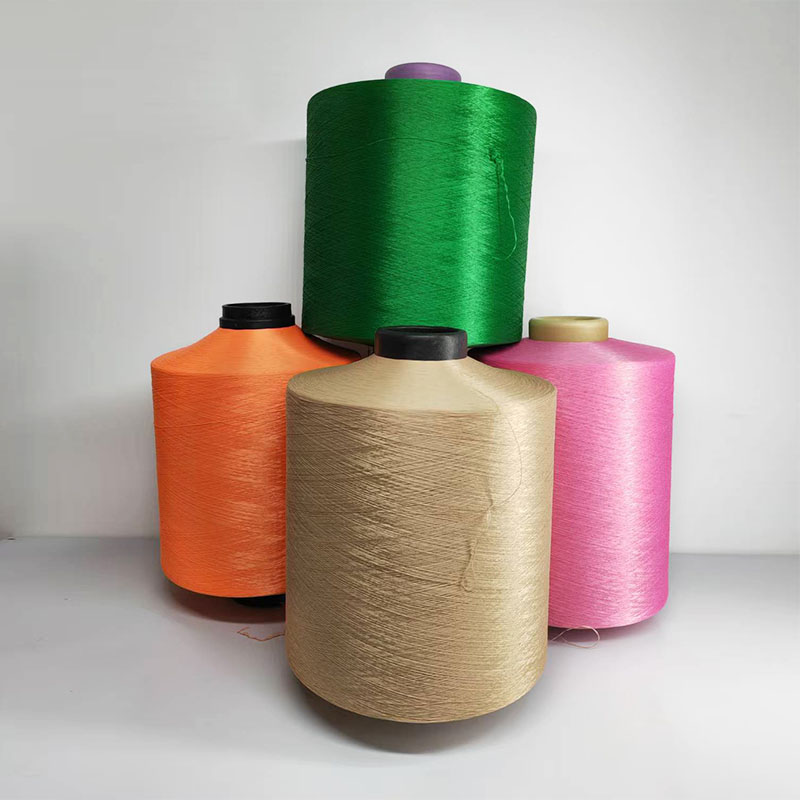
Polyester chips need to be dried (water content ≤ 0.005%) and melted (280-290℃) before entering the spinning process. In the spinning machine, the melt is extruded through a spinneret (aperture 0.2-0.4mm) to form filaments, which are cooled and solidified by side blowing, and then stretched (stretching multiples 3-5 times) to increase the molecular orientation, and finally wound into polyester raw yarn.
According to different processing techniques, raw materials can be converted into different types of polyester yarns: FDY (fully drawn yarn) uses one-step spinning and drawing, and the yarn has good gloss and high strength; POY (pre-oriented yarn) needs to be post-processed and drawn, which is suitable for making stretch yarn; DTY (stretched textured yarn) gives the yarn fluffiness and elasticity through twisting and shaping to meet the needs of knitted fabrics.
The influence of raw material characteristics on yarn performance
The crystallinity of polyester chips directly affects the elasticity of polyester yarn. The yarn made of chips with high crystallinity (40%-50%) is crisp but poor in elasticity, which is suitable for woven fabrics; chips with 0.5%-1% matting agent (titanium dioxide) can produce semi-matte and full-matte polyester yarns, which solves the aurora problem of ordinary polyester yarns and improves the texture of fabrics.
The impurity content in the raw materials is a key quality control point. The iron ion content must be less than 0.5ppm, otherwise it will cause the yarn to turn yellow; the content of oligomers must be less than 1.5% to avoid white powder pollution during weaving. By controlling the purity of raw materials, the breaking strength of polyester yarn can be stabilized at 4.5-5.5cN/dtex, meeting the high strength requirements of industrial textiles.
From petroleum derivatives to environmentally friendly recycled raw materials, the development of raw materials for polyester yarn has always been centered around performance improvement and sustainable development. Its diversified raw material system provides a wealth of choices for the textile industry.